Lessons Menu:
- Lesson 1 – Getting Started
- Lesson 2 - Choosing a Robotic Platform
- Lesson 3 - Making Sense of Actuators
- Lesson 4 - Understanding Microcontrollers
- Lesson 5 - Choosing a Motor Controller
- Lesson 6 – Controlling your Robot
- Lesson 7 - Using Sensors
- Lesson 8 - Getting the Right Tools
- Lesson 9 - Assembling a Robot
- Lesson 10 - Programming a Robot
Now, it is time to decide on the type if robot you are going to build. A custom robot design often starts with a “vision” of what the robot will look like and what it will do. The types of robots possible are unlimited, though the more popular are:
- Land wheeled, tracked, and legged robots
- Aerial planes, helicopters, and blimp
- Aquatic boats, submarines, and swimming robots
- Misc. and mixed robots
- Stationary robot arms, and manipulators
Land
Land-based robots, especially the wheeled ones, are the most popular mobile robots among beginners as they usually require the least investment while providing significant exposure to robotics. On the other hand, the most complex type of robots is the humanoid (akin to a human), as it requires many degrees of freedom and synchronizing the motion of many motors, and uses many sensors.
Wheeled Robots
Wheels are by far the most popular method of providing mobility to a robot and are used to propel many different sized robots and robotic platforms. Wheels can be just about any size, from a few centimetres up to 30 cm and more . Tabletop robots tend to have the smallest wheels, usually less than 5 cm in diameter. Robots can have just about any number of wheels, although 3 and 4 are the most common. Normally a three-wheeled robot uses two wheels and a caster at one end. More complex two wheeled robots may use gyroscopic stabilization. It is rare that a wheeled robot use anything but skid steering (like that of a tank). Rack and pinion steering such as that found on a car requires too many parts and its complexity and cost outweigh most of its advantages.Four and six wheeled robots have the advantage of using multiple drive motors (one connected to each wheel) which reduces slip. Also, omni-directional wheels or mecanum wheels, used properly, can give the robot significant mobility advantages. A common misconception about building a wheeled robot is that large, low-cost DC motors can propel a medium sized robot. As we will see later in this series, there is a lot more involved than just a motor.
Advantages
- Usually low-cost compared to other methods
- Simple design and construction
- Abundance of choice
- Six wheels or more rival a track system
- Excellent choice for beginners
Disadvantages
- May lose traction (slip)
- Small contact area (only a small rectangle or line underneath each wheel is in contact with the ground)
Tracked Robots
Tracks (or treads) are what tanks use. Although tracks do not provide added "force" (torque), they do reduce slip and more evenly distribute the weight of the robot, making them useful for loose surfaces such as sand and gravel. Also, a track system with some flexibility can better conform to a bumpy surface. Finally, most people tend to agree that tank tracks add an "aggressive" look to the robot as well.Advantages
- Constant contact with the ground prevents slipping that might occur with wheels
- Evenly distributed weight helps your robot tackle a variety of surfaces
- Can be used to significantly increase a robot’s ground clearance without incorporating a larger drive wheel
Disadvantages
- When turning, there is a sideways force that acts on the ground; this can cause
 damage to the surface the robot is being used on, and cause the tracks to wear
damage to the surface the robot is being used on, and cause the tracks to wear - Not many different tracks are available (robot is usually constructed around the tracks)
- Drive sprocket might significantly limit the number of motors that can be used.
- Increased mechanical complexity (idler placement and number, # of links) and connections
Legs
An increasing number of robots use legs for mobility. Legs are often preferred for robots that must navigate on very uneven terrain. Most amateur robots are designed with six legs, which allow the robot to be statically balanced (balanced at all times on 3 legs); robots with fewer legs are harder to balance. The latter require "dynamic stability", meaning that if the robot stops moving mid-stride, it might fall over. Researchers have experimented with monopod (one legged "hopping") designs, though bipeds (two legs), quadrupeds (four legs), andhexapods (six legs) are the most popular.Advantages
- Closer to organic or natural motion
- Can potentially overcome large obstacles and navigate very rough terrain
Disadvantages
- Increased mechanical, electronic and coding complexity (not the easiest way to get into robotics).
- Lower battery size despite increased power demands
- Higher cost to build
Advantages
- Remote controlled aircraft have been in existence for decades (so there is a large community, at least for the mechanics)
- Excellent for surveillance
Disadvantages
- The entire investment can be lost in one crash.
- Limited robotic community to provide help for autonomous control
Advantages
- Most of our planet is water, so there is a lot to explore and discover
- Design is almost guaranteed to be unique
- Can be used and/or tested in a pool
Disadvantages
- Robot can be lost many ways (sinking, leaking, entangled...)
- Most electronic parts do not like water (also consider water falling on electronics when accessing the robot after a dive)
- Surpassing depths of 10m or more can require significant research and investment
- Very limited robotic community to provide help
- Limited wireless communication options
Advantages
- Designed and built to meet specific needs
- Multi-tasking and can be comprised of modules
- Can lead to increased functionality and versatility
Disadvantages
- Possible Increased complexity and cost
- Often times, parts must be custom designed and built
Advantages
- Very simple to very complex design possibilities
- Easy to make a 3 or 4 degree of freedom robot arm (two joints and turning base)
Disadvantages
- Stationary unless mounted on a mobile platform
- Cost to build is proportional to lifting capability
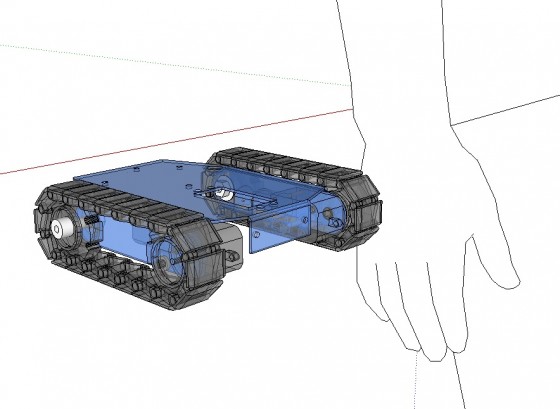
In our case, we have opted for building a robot that will provide the maximum exposure to robotics. A programmable tracked platform that can accommodate a variety of sensors and gripper sees ideal in this case, specially since we consider tank tracks are far cooler than wheels.
In order to keep the costs down, we opted to build a small desktop robot that will be able to roam indoors and on tabletops. We also have taken into consideration the fact that there are not many tracks available, and to keep things simple, we’ll only consider a single drive sprocket and single idler sprocket system, this should not be a problem since the robot will be very light weight.
The preliminary CAD below summarized the features describes so far.
Next, we will be choosing the right actuators (e.g. motors) for your robot.![]() For further information on learning how to make a robot, please visit the RobotShop Learning Center. Visit the RobotShop Community Forum in order to seek assistance in building robots, showcase your projects or simply hang-out with other fellow roboticists.
For further information on learning how to make a robot, please visit the RobotShop Learning Center. Visit the RobotShop Community Forum in order to seek assistance in building robots, showcase your projects or simply hang-out with other fellow roboticists.
This is a companion discussion topic for the original entry at https://community.robotshop.com/tutorials/show/how-to-make-a-robot-lesson-2-choosing-a-robotic-platform