Robot Arm Torque Calculator
The Robot Torque Arm Calculator is intended to help you choose the right motor for each joint of your robotic arm. The torque (T) required at each joint is calculated as a worst-case scenario (lifting weight at 90 degrees). Ensure your units are consistent. The most common units are kg-cm and oz-in. Take a look at the Robot Arm Torque Tutorial for more information.
- L: length from pivot to pivot.
- M: link mass
- A: Actuator (servo or other) mass. Note: same units as for link masses.
- A1: can represent the load being lifted.
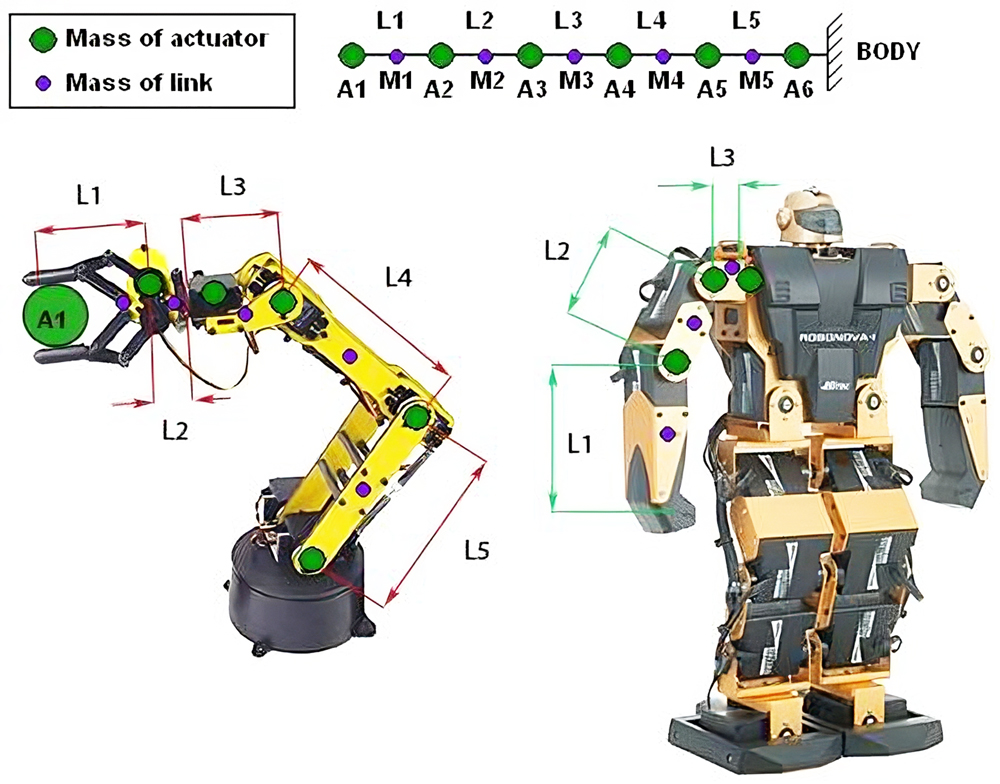
Use the image above to help you determine which torque corresponds to which joint. Note the numbering starts with the extremity of the arm, so the final torque is the one lifting the entire arm (start from A1 being the load you wish to carry at full reach.). The torque shown is the RATED TORQUE you can use for your search. Note that should this be the stall torque, the arm would not be able to lift itself at full extension with a payload.
| L: | [cm] | M: | [kg] | A: | [kg] | T: | [kg cm] |
| L1: | M1: | A1: | T1: | ||||
| L2: | M2: | A2: | T2: | ||||
| L3: | M3: | A3: | T3: | ||||
| L4: | M4: | A4: | T4: | ||||
| L5: | M5: | A5: | T5: | ||||
| L6: | M6: | A6: | T6: |


