Hi!
I am designing a skid-steering robot, with a total weight of around 25 kg. It consists of four 160 mm wheels, where the two wheels on each side turn at the same speed. My wheel track of the robot is limited due to space requirements and is 0.45 m. My question is, how can I estimate the optimal wheelbase length taking into account stability and maneuverability?
Thank you so much in advance for your help!
2 Likes
@jakimovska Estimating a wheelbase would depend on many factors, including:
- Overall weight of the robot (known)
- Number of wheels (known) - which gives the weight per wheel
- Estimated turning radius & wheel base / dimensions
- The wheel’s cross-sectional profile (to estimate contact area)
- etc.
The issue with 4WD skid steering is that the wheels are forced left and right against whatever surface they are on (much in the same way a tank track destroys the terrain when it rotates). This creates an added linear force beyond just the rotational force which the drive motors need to overcome. When it comes to rotating, the closer the wheels are aligned (tangentially) to the turning radius, the more easily they will rotate. As the wheels become more tangential to the turning radius, the more sideways force they face and scrape against the surface. Don’t have any equations for you unfortunately, but hope this provides some insight.
1 Like
Thank you for your reply!
When looking into the turning radius, from geometries:
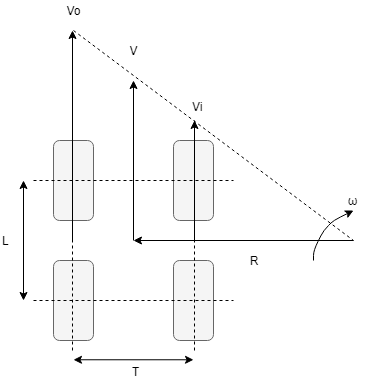
The turning radius is dependent on the track width - from geometry (without taking into account slipping).
However, I am not sure how the wheelbase plays a role in the turning radius. I do understand that the longer the wheelbase the more stability it has and less maneuverability, but I am not sure how this can be expressed mathematically.
1 Like
Nothing immediately comes to mind, so if someone has suggestions, they are most welcome here. If not, I’ll keep an eye out.
1 Like
from my experience:
- a longer wheelbase will make steering more difficul --> , so the shorter, the better, as this will put less lateral forces on the wheels during turning.
- a shorter wheel base negatively affects longitudinal driving --> the vehicle becomes more sensitive to terrain unevenness, so will drive much more bumpy / wiggling in longitudinal direction. So, for stable driving --> the longer the wheel base the more stable the vehicle
- there might be some literature in how these parameters affect driving control and localisation, but so far I am not aware of specific notions regarding design
- Mostly, the design will be more constrained by other factors like total vehicle dimensions, available space etc, and within that, the design is improved. the result is than combining and weighing all these factors to make a suitable construction
hope this helps you a little. Finding the optimal value is useless in general, it is sufficient to be in a suitable range…



