Unitree Humanoids Comparison: How to choose the right humanoid for you

Comparing the G1 & H1 Humanoids
Unitree Robotics, a prominent robotics company, has expanded its product line beyond quadruped robots to include humanoid robots, notably the G1 and H1 models. These humanoid robots are engineered to perform a variety of tasks, showcasing advanced mobility, dexterity, and adaptability.
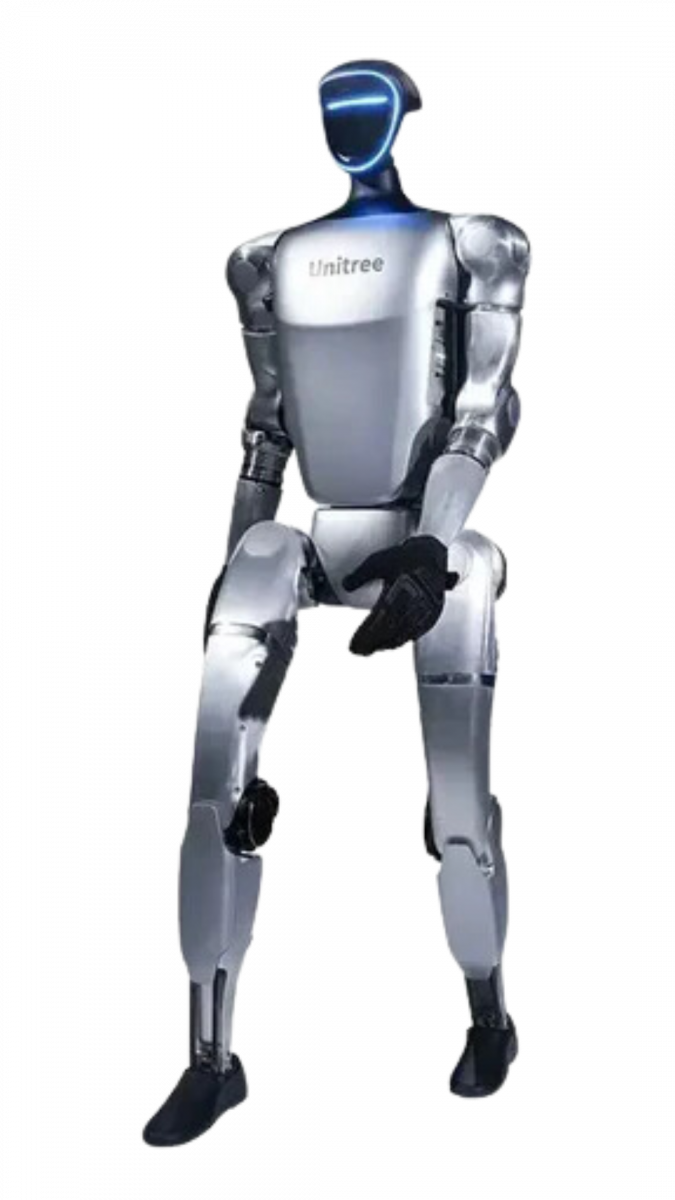
The Unitree G1 is a compact humanoid robot standing ~127 cm tall and weighing around 35 kg. It features 23 to 43 degrees of freedom, depending on the configuration, allowing for a wide range of movements. Equipped with 3D LiDAR and depth cameras, the G1 can perform tasks such as jumping, walking at speeds over 4.4 mph, and climbing stairs. Its three-fingered hands enable it to handle delicate objects, making it suitable for research and educational purposes. The G1 is one of the first humanoids of its size to be commercialized, and even better at a relatively affordable price. Ideal for institutions and developers, or even organizations like RoboCup, the G1 is an excellent choice.
In contrast, the Unitree H1 is a full-sized humanoid robot, standing about 180 cm tall and weighing approximately 47 kg. It boasts a peak torque density of 189 N.m/kg and a maximum joint torque of 360 N.m, providing exceptional power and agility. The H1 is capable of running at speeds up to 3.3 m/s and is equipped with 3D LiDAR and depth cameras. Its design allows for autonomous navigation in complex terrains, making it suitable for advanced research and development applications.
In this blog post, we will compare the Unitree G1 and H1 humanoid robots and their different versions. Understanding the differences between these models will assist you in selecting the robot that best aligns with your project's requirements.This side-by-side comparison table for Unitree’s G1 and H1 humanoids. Remember that real-world performance and features can vary depending on your specific configuration and usage.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feature / Spec | G1 "Basic" |
G1 EDU U1 "Standard" |
G1 EDU U2 "Plus" |
G1 EDU U3 "Ultimate A" |
G1 EDU U4 "Ultimate B" |
G1 EDU U5 "Ultimate C" |
H1 | H1-2 |
| CANADA / USA | RB-UNT-51 | RB-UNT-50 | RB-UNT-48 | RB-UNT-56 | RB-UNT-49 | RB-UNT-86 | RB-UNT-47 | RB-UNT-46 |
| UK | RB-UNT-57 | RB-UNT-87 | RB-UNT-37 | RB-UNT-91 | RB-UNT-61 | RB-UNT-77 | RB-UNT-93 | RB-UNT-78 |
| EU | RB-UNT-100 | RB-UNT-89 | RB-UNT-28 | RB-UNT-64 | RB-UNT-92 | RB-UNT-70 | RB-UNT-74 | RB-UNT-73 |
| JP | RB-UNT-51 | RB-UNT-50 | RB-UNT-48 | RB-UNT-56 | RB-UNT-49 | RB-UNT-86 | RB-UNT-47 | RB-UNT-46 |
| Total DoF (joint freedom) |
23 | 23 | 29 | 43 | 43 | 41 | ||
| Waist DoF | 1 | 1 | 3 DoF | |||||
| Single Arm DoF | 5 | 7 (both arms upgraded) |
4 | 7 | ||||
| Dexterous Hands Choice | NO | NO | NO | 2× Dex3-1 force-controlled 3-finger dexterous hands |
2× Dex3-1 force-controlled 3-finger dexterous hands with tactile sensor |
2× Inspire 5-finger dexterous hands RH56DFQ-2R, RH56DFQ-2L |
Optional: Inspire 5-finger dexterous hands (including one wrist DoF) Must purchase with H1 RB-UNT-72 (L), RB-UNT-63 (R) |
|
| CPU / GPU (Dev. Module) |
NO | Built-in 100Tops NVIDIA Jetson Orin AI algorithm & technical support. |
1× std Intel Core i5-1235U (locomotion) |
|||||
| Max Torque Knee Joint [1] |
90 N·m | 120 N·m | Knee Torque About 360N.m, Hip Joint Torque About 220N.m, Ankle Torque About 59N.m, Arm Joint Torque About 75N.m |
60N.m for knee joint 220N.m for hip joint 45N.m for ankle joint 75N.m for arm joint |
||||
| Weight (with battery) |
About 35 kg | About 35 kg+ | About 47 kg | About 73 kg | ||||
| Secondary Dev. [3] | NO | YES | YES | |||||
| Extra Joint Movement Space |
Waist: Z±155° Knee: 0~165° Hip: P±154°, R-30~+170°, Y±158° Wrist: NONE |
Waist: Z±155°, X±45°, Y±30° Knee: 0~165° Hip: P±154°, R-30~+170°, Y±158° Wrist: P±92.5°, Y±92.5° |
||||||
| Warranty Period [4] | 8 Months | 1 Year | ||||||
| Height × Width × Thickness (Stand) |
1320×450×200 mm | (1520+285) mm × 570 mm × 220 mm | ||||||
| Height × Width × Thickness (Folded) |
690×450×300 mm | |||||||
| Single Leg DoF | 6 | 5 (Hip×3 + Knee×1 + Ankle×1) | 6 (Hip×3 + Knee×1 + Ankle×2) | |||||
| Joint Output Bearing | Industrial-grade crossed roller bearings (high precision, high load capacity) |
|||||||
| Joint Motor | Low-inertia, high-speed internal rotor PMSM | |||||||
| Arm Max Load [2] | About 2 kg | |||||||
| Calf + Thigh Length | 0.6 m | Length of thigh: 400mm; Length of calf: 400mm |
||||||
| Arm Span | About 0.45 m | Length of big arm: 338mm; Length of small arm: 338mm; |
||||||
| Full-Joint Hollow Electric Routing | YES | |||||||
| Joint Encoder | Dual encoder | |||||||
| Cooling System | Local air cooling | |||||||
| Power Supply | 13-string lithium battery | |||||||
| Dual Battery | No | YES | ||||||
| Sensing Sensor | 3D LIDAR: LIVOX-MID360 Depth Camera: Intel Realsense D435i |
3D LIDAR: LIVOX-MID360 Depth Camera: Intel Realsense D435i |
||||||
| 4 Microphone Array | YES | NO | ||||||
| Speaker | 5W Stereo | NO | ||||||
| WiFi 6, Bluetooth 5.2 | YES | NO | ||||||
| Smart Battery (Quick Release) |
9Ah | 15Ah (0.864 KWh), Max 67.2V RB-UNT-14 |
||||||
| Charger | 54V, 5A | Fast Charger RB-UNT-53 (EU), RB-UNT-83 (USA), RB-UNT-45 (UK) |
||||||
| Manual Controller | Included | Included RB-UNT-82 |
||||||
| Battery Life | 2h | 2h | ||||||
| Upgraded Intelligent OTA | YES | YES | ||||||
| Mobility | Walking speed: 2 m/s | Walking speed: >1.5 m/s Moving speed of 3.3 m/s (world record) Potential >5 m/s |
||||||
| Gantry | NO | Included (Only G1 EDU series includes one free gantry) | Included RB-UNT-55 | |||||
| Voice Function | English & Chinese via "Benben Dog" App function | NO | ||||||
|
[1] The maximum torque stated generally applies to the knee joint; other joints may vary. [2] Arm Max Load depends on servo torque, link length, and speed. [3] Secondary Development refers to user-accessible APIs, open SDK, or dev kits. [4] Warranty Period can vary by region; always confirm with your supplier. [5] Extended Options: 1× additional Orin NX; 1× additional Intel Core i7; 1× additional AGX (max 2 units 550Tops); RB-UNT-102 (Orin NX), RB-UNT-76 (275 TOPS), RB-UNT-94 (550 TOPS) |
||||||||
What These Humanoids Can Do
- Walking: Up until just recently, getting a humanoid of child / teen / adult size to balance, walk, turn and move without constantly falling, let alone commercialize to the general public was quite an accomplishment.
- Grasping and manipulation: With multiple degrees of freedom in each arm and optional dexterous hands, they could be programmed to pick up objects or perform simple assembly tasks.
- Autonomous navigation (with sensors): Each robot includes LiDAR and depth cameras which could be used to help them map their environments and avoid obstacles.
- Voice commands: Selected models integrate microphones and basic voice interaction through companion apps (e.g., “Benben Dog”).
- Remote control & teleoperation: A manual controller plus advanced connectivity allows you to guide the robot in real time.
- Research and development platform: Models with integrated or optional CPUs/GPUs (Jetson Orin, Intel i7, etc.) support AI, robotics research, or custom software projects.
What They Cannot Do
- Know” how to perform a variety of tasks: Humanoid robots are not yet at the point where they can easily recognize objects, “know” where rooms are and how to navigate to them or where objects can be found or placed.
- Replicate human dexterity: Even advanced hands have limitations; tasks requiring extreme fine-motor control may not be feasible.
- Operate without supervision: They rely on battery power and have sensor range limitations; supervision and recharging are necessary.
- Operate without supervision in all conditions: They rely on battery power and have sensor range limitations; supervision and recharging are necessary.
- Handle extreme climates or hazardous materials: Like most robotics, they need proper insulation and environment-specific modifications for harsh conditions.
- Speak and understand complex language: Voice features are typically limited to pre-set commands or simple interactions.This is advancing quickly with large language models though.
- Replace heavy lifting equipment: Although they can carry light loads in their arms, they aren’t designed for large industrial payloads.
What’s Next?
Whether you’re using these humanoids for advanced research, light industrial tasks, or educational demos, the G1 and H1 models offer impressive capabilities and customization options. Always be mindful of their limitations, and make sure to consider factors like battery life, payload requirements, and terrain challenges in your planning process.
As humanoid robots, advanced machine vision and AI merge, humanoids might be able to “teach themselves” how to do tasks, or “learn by watching”. Their dexterity will likely improve, as will their speech and task comprehension.
If these humanoids might be a bit complex or out of budget, Unitree offers a range of more affordable quadruped “dog” type robots. The comparison between models can be found here.
Thanks for helping to keep our community civil!
This post is an advertisement, or vandalism. It is not useful or relevant to the current topic.
You flagged this as spam. Undo flag.Flag Post



